BLE Lock
User Guide of BLE Lock SDK (Public Edition)
1 Overview
The Tuya common Bluetooth door lock is a common version of Tuya Bluetooth door locks. The Tuya common Bluetooth door lock SDK allows you to connect your lock business app to the TuyaSmart app and Tuya Smart platform through Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE).
Tuya provides this document to help you resolve all issues during embedded software development. If you encounter a problem, read this document first.
To get quickly started, see section 5 that describes serial interface commands for hardware simulation and a quick experience of Tuya lock products. You may also use the example for subsequent debugging.
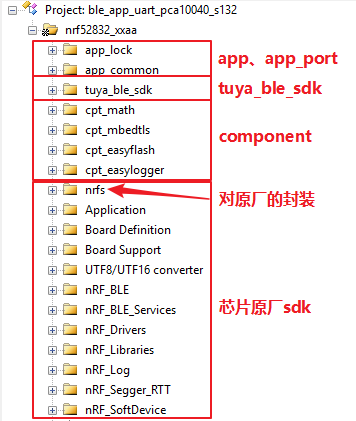
2 Software Architecture
Tuya BLE products use the common, basic Bluetooth network pairing protocol, which implements the common Bluetooth product network pairing process and basic data communications. For details about the protocol, see Tuya Common BLE SDK Protocol. The source code is stored in the tuya_ble_sdk folder. If you use the demo platform, ignore this protocol because Tuya has migrated the protocol. If you use a new platform, migrate this protocol. For details, see Tuya Common BLE SDK Development Guide.
In addition to the common network pairing protocol, Tuya defines a set of data point (DP) protocols for lock products. These protocols describe the communications logic between lock business and a mobile app. To facilitate development, Tuya has encapsulated these DP protocols. For details about the source code, see the app-layer files lock_dp_parser and lock_dp_report. For details about the protocol content, see Tuya BLE Lock DP Specifications.
The preceding Tuya Bluetooth product network pairing, communications, and lock service implementation are the main framework. In addition to the main framework, there are some important support components: third-party components and Tuya components. Third-party components implement common features such as storage and debugging, whereas Tuya components implement private features such as authorization and product test.
Third-party components include easyFlash, easyLogger, and mbedtls. If you use the demo platform, ignore these components because Tuya has migrated them. If you use a new platform, simply migrate the easyFlash and easyLogger components and do not alter the mbedtls component. The mbedtls component mainly contains encryption APIs.
Tuya components are common source code packages and apply to most Tuya's low-power single-node BLE products. This document describes their application in door lock apps and provides reference for applications in other apps. Tuya components include the components of authorization product test, Over-the-Air (OTA) upgrades, local storage management, and complete device tests. The authorization product test component is used for burning and verification of parameters such as the MAC address, authkey, and device ID that the common network pairing protocol requires. For details, see Tuya Common BLE Authorization Product Test Protocol. The OTA upgrade component implements the Tuya-defined Bluetooth OTA protocol. If you use a non-demo platform, migrate this component. For details, see Tuya Common BLE SDK Protocol. The local storage management component implements the local storage logic of lock apps and also applies to other apps. The complete device test component tests overall product functions. For details, see Tuya Common BLE Complete Device Test Protocol.
In addition to the main framework and support components, an isolation layer called "app_port" is deployed between the app layer and other layers to improve compatibility of the app layer (involving Tuya components). At the app layer, you can only view bottom-layer APIs (their names start with "app_port") that have been encapsulated at the isolation layer and app layer APIs.
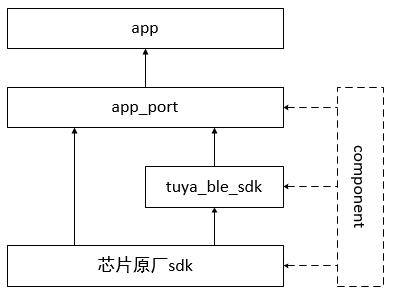
2.1 App
2.1.1 app_lock
This folder is used for lock business functions at the app layer and applies only to lock products.
lock_common: not classified.
lock_dp_parser: DP parsing. Data flows from a mobile phone to a device. For details, see Tuya BLE Lock DP Specifications.
lock_dp_report: DP reporting. Data flows from a device to a mobile phone. For details, see Tuya BLE Lock DP Specifications.
lock_hard: customer hardware APIs and serial interface commands for hardware simulation (used for a quick start or debugging).
lock_test: complete device test. For details, see Tuya Common BLE Complete Device Test Protocol.
2.1.2 app_common
This folder implements common functions at the app layer and applies to various Bluetooth products.
app_common: not classified.
app_flash: local storage management.
app_ota: OTA upgrade functions. For details, see Tuya Common BLE SDK Protocol.
app_test: product test authorization. For details, see Tuya Common BLE Authorization Product Test Protocol.
app_port: For details, see section 2.2 "app_port."
2.2 app_port
app_port is used for bottom-layer API encapsulation and provides unified names and management of all APIs that the app layer may use, ensuring an independent app layer and facilitating migration.
2.3 tuya_ble_sdk
tuya_ble_sdk is a common network pairing SDK for Tuya BLE products. It implements network pairing and basic communications between BLE devices and a mobile app.
Implementation protocol: For details, see Tuya Common BLE SDK Protocol.
Development guide: For details, see Tuya Common BLE SDK Development Guide.
2.4 Chip Vendor's SDK
The demo project uses Nordic's SDK nRF5_SDK_15.3.0_59ac345.
2.4.1 NRFS (Applies Only to the Demo Project)
NRFS encapsulates APIs of the Nordic SDK.
nrfs_common: not classified
nrfs_scan_adv: scanning and advertising
nrfs_ble: BLE parameters
nrfs_svc: service and feature values
nrfs_uart: serial interfaces
nrfs_timer: timer
nrfs_flash: flash
nrfs_gpio: GPIO
nrfs_test: used for R&D and test
2.5 Components
This section describes third-party components.
2.5.1 cpt_math
Implements common mathematical algorithms, such as checksum, CRC-16, CRC-32, and byte reversal.
Is a pure C language library. You do not need to migrate or alter this component, regardless of the platform you use.
2.5.2 cpt_mbedtls
Implements common encryption algorithms, such as AES-128 in ECB mode, AES-128 in CBC mode, and MD5.
Is used for encrypting data in tuya_ble_sdk.
Is a pure C language library. You do not need to migrate or alter this component, regardless of the platform you use.
2.5.3 cpt_easyflash
Implements the flash-based key value storage mechanism, mainly by using the following four APIs. For details about the APIs, see the code comment.
easyflash_init();
ef_set_env_blob(key, buf, size) ;
ef_get_env_blob(key, buf, size) ;
ef_del_env(key) ;
If you use the demo platform, this component has been migrated and you can use it directly. If you use a new platform, migrate this component and enable at least functions of the preceding four APIs.
For details about the source code and guide, visit https://github.com/armink/EasyFlash.
2.5.4 cpt_easylogger
Implements the SDK log printing mechanism, mainly by using the following two APIs. For details about the APIs, see the code comment. log_d(); elog_hexdump(name, width, buf, size);
If you use the demo platform, this component has been migrated and you can use it directly. If you use a new platform, migrate this component and enable at least functions of the preceding two APIs.
For details about the source code and guide, visit https://github.com/armink/EasyLogger.
3 Important Parsing
3.1 Local Storage Management
tuya_ble_sdk requires 16 KB flash memory to store system information related to authorization and tuya_ble_sdk. The flash memory must be separately allocated and cannot be used for other purposes. The memory start address is TUYA_NV_START_ADDR.
By default, the app layer requires 16 KB flash memory to store offline records and other app data (key-value storage structure based on easyFlash). You can use the remaining space and need to adjust the occupied flash memory size based on actual usage. The memory start address is EF_START_ADDR, and the occupied memory size is ENV_AREA_SIZE. Related APIs are as follows: - uint32_t app_port_kv_set(const char *key, const void *buf, size_t size); - uint32_t app_port_kv_get(const char *key, void *buf, size_t size); - uint32_t app_port_kv_del(const char *key);
The above mentioned flash memory contains only the user data storage area and does not contain the code storage area.
Local storage includes hardware, event, and settings storage. The storage logic is implemented in the app_flash.c file.
3.1.1 Hardware Storage
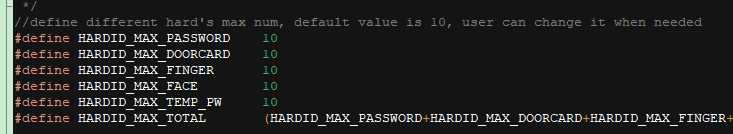
The app layer has implemented the management logic for hardware storage and can store up to 256 hardware devices. A hardware device support one type of door opening methods, and the app layer can store four door opening method types. You can adjust the maximum number of stored door opening methods of each type based on actual requirements. By default, each type supports 10 door opening methods, as shown in the following figure.
3.1.2 Event Storage
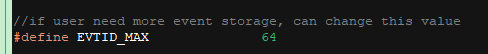
The app layer has implemented the management logic for event storage and can store "EVTID_MAX" events. You can adjust the maximum number of events that can be stored based on actual requirements. If the size of stored event data exceeds the allocated flash memory size, the flash memory needs to be re-allocated. By default, up to 64 events can be stored, as shown in the following figure.
3.1.3 Settings Storage
The app layer has implemented the management logic for settings storage to store setting items related to the door lock. For details, see the "lock_settings_t" structure.
To modify a default door lock setting, modify the related parameter in "lock_settings_default" of the API.
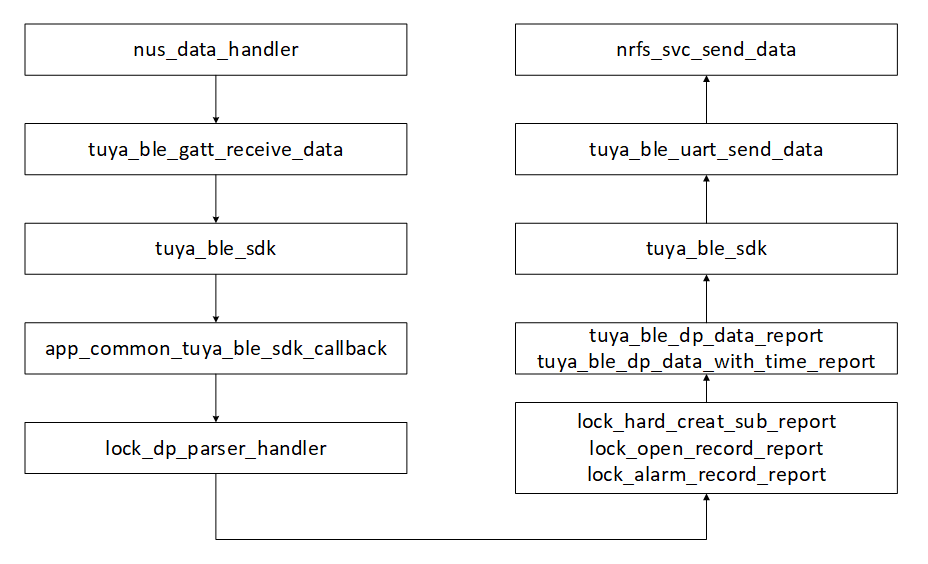
3.2 Bluetooth Data Channel
3.3 DP Parsing
The lock_dp_parser and lock_dp_report files are used for DP parsing based on Tuya BLE Lock DP Specifications. These files describe this protocol specification document in C language.
The lock_dp_parser.c file is used for parsing lock DP data received through Bluetooth. If the parsed data is related to hardware, the data will be sent to the lock_hard.c file, which contains the API for DP data and local logic and deserves your most attention.
The lock_dp_report.c file is used for reporting DP data through Bluetooth. To report required data in the local logic, invoke the encapsulated API in this file.
3.4 OTA Upgrade
The OTA upgrade component is stored in the app_ota file. The demo implementation process applies to the demo platform. It is only for your reference if you use a new platform. To perform an OTA upgrade of the new platform, use the communications protocol that Tuya provides. To put it simply, Tuya provides the Tuya Smart platform to store OTA upgrade files and data communications protocols. You need to implement the local flash storage logic for the OTA upgrade component. The logic has been implemented in the demo project.
3.5 Product Test
Product tests of a Tuya Bluetooth lock product include the following:
1. Authorization test: inspects product information and burns the MAC address, device ID (or UUID), and authkey.
2. Complete device test: includes the mandatory RF received signal strength indicator (RSSI) test and optional tests of other functions.
The purpose of an authorization product test is authorization. It involves inspection of product information and burning of important parameters used in the common network pairing protocol, including the MAC address, device ID (or UUID), and authkey. It is the base for product security. The complete device test tests product peripherals to ensure a low defect rate during production. Tuya has provided a complete Bluetooth-based product test protocol, product test Dongle firmware, and product test microcontroller unit (MCU) for complete device tests. For details about the product test, see related protocol documents.
4 Demo
4.1 Basic Demo Information
Chip: nRF52832
SDK: nRF5_SDK_15.3.0_59ac345
IDE: μVision V5.28.0.0
Project: ble_app_uart
Serial interface: rx-8 and tx-6 (for authorization test)
Debugging information: RTT_viewer
4.2 Demo Project Architecture
4.3 Firmware Burning
Double-click load_softdevice_bootloader_app.bat in **\nRF5_SDK_15.3.0_59ac345\examples\ble_peripheral\ble_app_uart\pca10040\s132\arm5_no_packs\hex**.
The preceding method burns the softdevice, bootloader, and app. To burn only the app, use keil download.
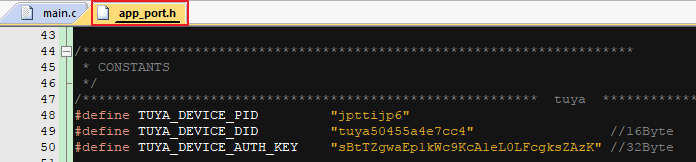
4.4 License Application
Contact your Tuya business manager and apply for a license based on Bluetooth Door Lock SDK License Application Process. For official projects, please use the license applied by the project manager for debugging (re-download the firmware after the chip is completely erased to take effect)! Product id, authkey, and device id are modified as shown in the following figure:
4.5 OTA Upgrade Process
Modify the firmware version. For details about the firmware version rules, see Tuya Common BLE SDK Protocol. The following figure shows the app_common.h file.
 Note: On some platforms, some platform-related key parameters also need to be modified before an OTA upgrade.
Note: On some platforms, some platform-related key parameters also need to be modified before an OTA upgrade.Recompile the project. Locate the tuya_ble_lock_common_nRF52832_xx.xx.bin file in \nRF5_SDK_15.3.0_59ac345\examples\ble_peripheral\ble_app_uart\pca10040\s132\arm5_no_packs\ota.
Log in to the Tuya Smart platform. On the Product page, click the product to be operated. On the displayed product page, click Extensions and click Settings next to Firmware Updates Center. Click New Firmware Update, enter the firmware information, and click OK. If you do not have the permission to create firmware, contact your Tuya business manager. To check the product's firmware version and virtual ID, do as follows: Open the TuyaSmart app and pair it with the Bluetooth device. Tap the edit icon in the upper right corner of the device page. On the displayed page, tap Check for Firmware Upgrades. A pop-up box shows the current firmware version. Tap Confirm. Tap Device Information, copy the virtual ID, and send it to your PC.
Tap Check for Firmware Upgrades in the app again to update the firmware. If the update fails, retry or verify the firmware.
5 Hardware Simulation Using Serial Interface Commands
To debug and verify solution feasibility conveniently and quickly, use simple serial interface commands to simulate various hardware door opening methods and other commands.
5.1 Serial Interface Command Format
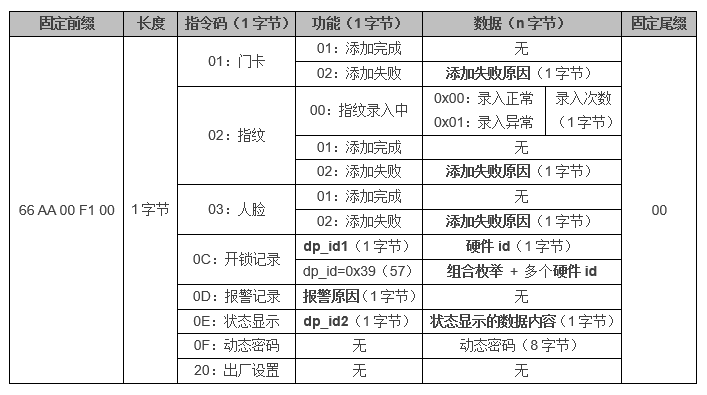
Recording failure causes
For details, see the recording failure causes part in section 3.1.1 of Tuya BLE Lock DP Specifications.
dp_id1
For details, see the dp_id part in section 3.2 of Tuya BLE Lock DP Specifications.
Hardware ID
The default value is 0x01. The value varies depending on the dp_id value.
For details, see the data content and value ranges part in section 3.2 of Tuya BLE Lock DP Specifications.
Alarm reasons
For details, see the alarm reasons part in section 3.2 of Tuya BLE Lock DP Specifications.
dp_id2
For details, see the dp_id part in section 3.3 of Tuya BLE Lock DP Specifications.
Status display content
For details, see the data content and value ranges part in section 3.3 of Tuya BLE Lock DP Specifications.
5.2 Example
Prepare a Nordic PCA10040 (recommended) or a development board with the nRF52832 chip and the same serial interfaces as the PCA10040 (RX = 8 and TX = 6). Connect the development board to a PC through J-Link and open the RTT Viewer debugging window.
Access \nRF5_SDK_15.3.0_59ac345\examples\ble_peripheral\ble_app_uart\pca10040\s132\arm5_no_packs\hex, and double-click load_softdevice_bootloader_app.bat to download the firmware. If the script execution fails, install JLink_Windows_V652e.exe and try again. After the command is executed, the debugging window will display a log.
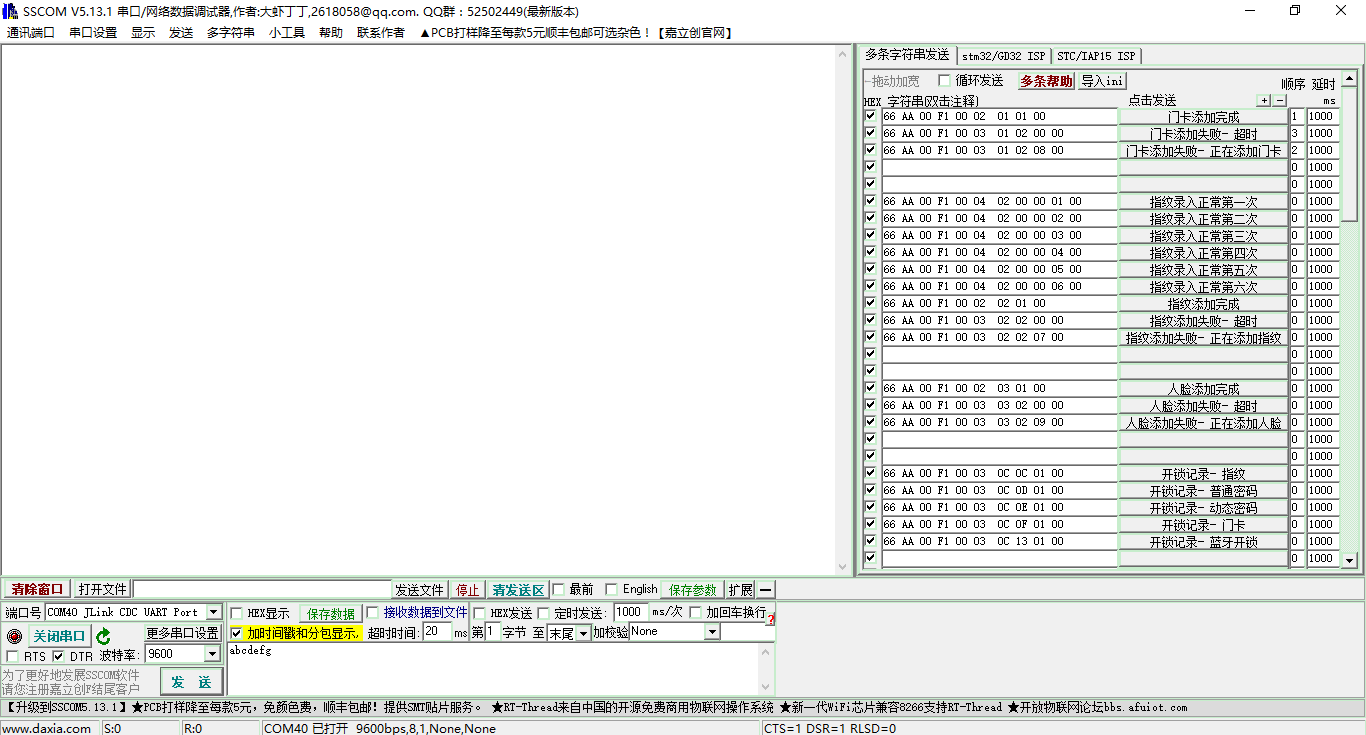
Double-click sscom5.13.1.exe in \tuya_ble_lock_sdk\tools\uart_simulate_hard\SSCOM.
Click the Multi-string button. Some serial interface commands mentioned in section 5.1 are automatically entered in the right text box of the software.
Set the serial interface baud rate to 9600 bit/s and use serial interface commands to simulate the hardware, as shown in the following figure.
Open the TuyaSmart app. Tap the plus sign (+) in the upper right corner and tap Auto Scan. Tap Start Scanning, select the Tuya common door lock, and tap Next. Tap Add (optional). Wait until the binding is completed.
Open the Tuya common door lock page and tap Door Opening with Mobile Phone to view logs about door opening with the mobile phone. Choose Door Opening Records > Fingerprint on the serial interface debugging assistant. "fingerprint unlock" is displayed in the TuyaSmart app. Use other functions as needed.
Last updated